What Causes Mobility Issues in the Elderly and Can They Be Prevented or Managed?
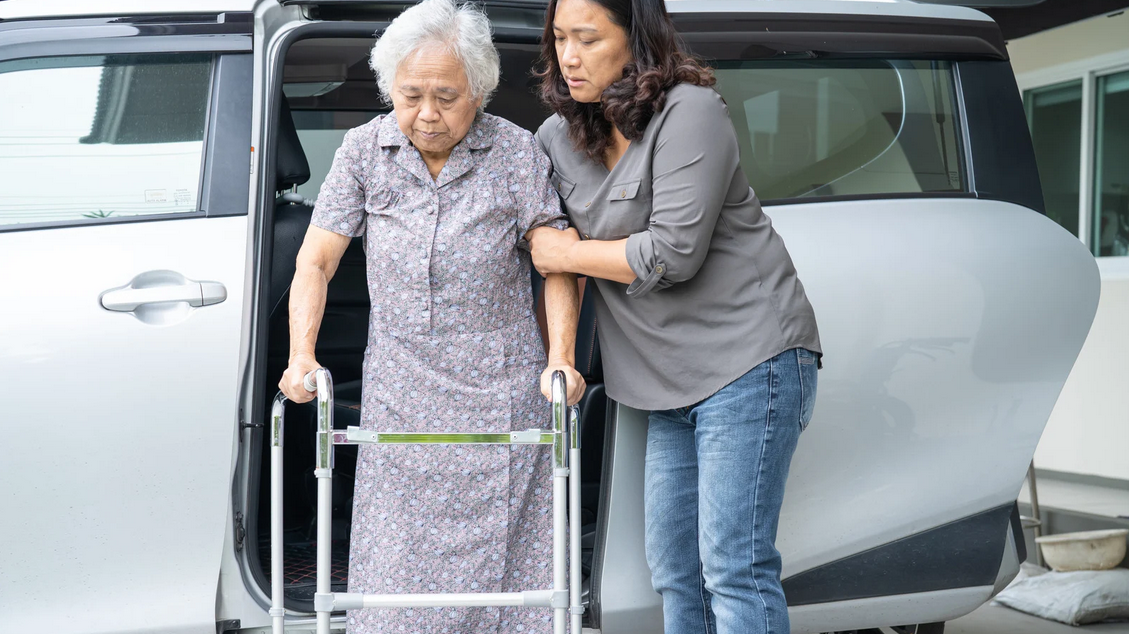

Maintaining mobility is crucial for elderly individuals as it directly impacts their independence and overall quality of life. However, various factors can contribute to mobility issues in older people. In this article, we’ll explore the common causes of mobility issues in the elderly and discuss strategies to prevent and manage them effectively.
Age-related Factors
As individuals age, they experience certain physiological changes that can affect their mobility. Musculoskeletal changes like osteoarthritis, osteoporosis, and joint stiffness often lead to pain, reduced range of motion, and difficulty performing daily activities.
A. Musculoskeletal Changes
Here are some of the common musculoskeletal changes that affect mobility:
- Osteoarthritis: This is a degenerative joint disease characterized by the breakdown of cartilage. This condition commonly affects weight-bearing joints like the knees, hips, and spine, causing pain, swelling, and limited mobility.
- Osteoporosis: It is a condition characterized by decreased bone density and strength, making bones more susceptible to fractures. Fragile bones increase the risk of falls and subsequent mobility limitations.
- Joint stiffness and reduced flexibility: With age, joints may become stiffer, leading to reduced flexibility. This stiffness can make it challenging to perform simple movements and tasks, hampering overall mobility.
B. Neurological Changes
Neurological changes can also contribute to mobility issues in the elderly. Conditions such as peripheral neuropathy, Parkinson’s disease, and stroke-related impairments affect the nervous system, leading to balance problems, muscle weakness, and coordination difficulties.
- Peripheral neuropathy: It is a nerve disorder characterized by damage to the peripheral nerves. This condition can result in numbness, tingling, and muscle weakness in the extremities, making it harder for seniors to walk and maintain balance.
- Parkinson’s disease: This is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder that affects movement and coordination. Symptoms include tremors, stiffness, and difficulty initiating and controlling movements, leading to mobility challenges.
- Stroke-related impairments: Stroke can cause neurological damage that affects mobility. The location and severity of the stroke determine whether individuals may experience muscle weakness, paralysis, or difficulties with coordination and balance.
Chronic Health Conditions
Several chronic health conditions prevalent in the elderly can contribute to mobility issues. Cardiovascular diseases, respiratory illnesses, and metabolic disorders are among the common culprits.
A. Cardiovascular Diseases
Diseases associated with the cardiovascular system affect the heart and blood vessels, compromising blood flow to various body parts. Two cardiovascular conditions that commonly impact mobility in the elderly are peripheral artery disease and heart failure.
- Peripheral artery disease: When blood flow to the legs and arms is restricted or blocked, it is known as peripheral artery disease. Reduced blood flow can lead to pain, cramping, and limb weakness, limiting mobility.
- Heart failure: This is a chronic condition where the heart cannot pump blood efficiently. Fatigue, shortness of breath, and fluid retention can significantly impact an individual’s ability to engage in physical activities, affecting mobility.
B. Respiratory Conditions
Respiratory conditions, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma, can hinder the elderly’s ability to breathe adequately and engage in physical activities, thus impacting their mobility.
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): COPD is a progressive lung disease characterized by airflow limitation. Individuals with COPD may experience shortness of breath, chronic coughing, and reduced stamina, making it difficult to engage in physical activities and maintain mobility.
- Asthma: It is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects the airways, leading to breathing difficulties. Elderly individuals with asthma may experience wheezing, coughing, and shortness of breath, limiting mobility and overall physical capacity.
C. Metabolic Disorders
Metabolic disorders, such as diabetes and obesity, can contribute to mobility issues in older adults by affecting various systems in the body.
- Diabetes: This is a chronic condition characterized by high blood sugar levels. Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to nerve damage (diabetic neuropathy) and circulatory problems, resulting in reduced sensation, muscle weakness, and compromised mobility.
- Obesity: This strains the musculoskeletal system excessively, making movement more challenging. Additionally, obesity is associated with an increased risk of developing conditions like osteoarthritis and cardiovascular diseases, further affecting mobility.
Injuries and Accidents
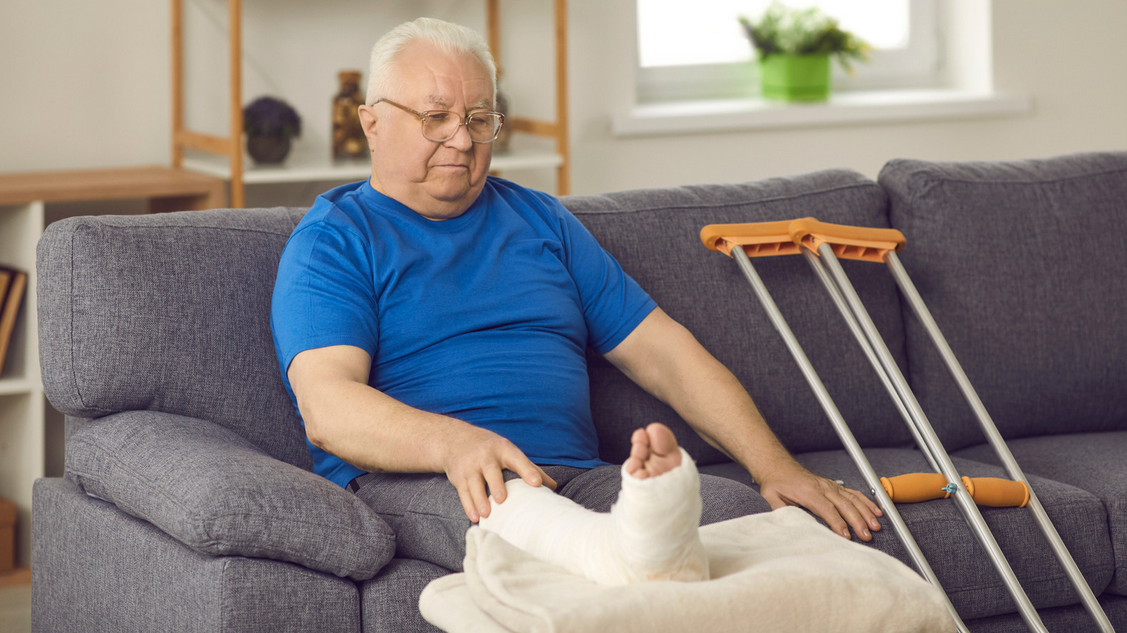

Injuries and accidents, particularly falls, are significant contributors to mobility issues among the elderly. Environmental hazards and age-related factors play a crucial role in these incidents.
A. Falls
Falls are a leading cause of injuries and mobility limitations among older adults. Environmental hazards, such as uneven surfaces, poor lighting, and cluttered spaces, can increase the risk of falls. Additionally, age-related factors like decreased balance and coordination make seniors more vulnerable to falls.
- Environmental hazards: Uneven flooring, loose rugs, and walkway obstacles can pose significant fall risks. Identifying and addressing such threats is essential to prevent falls and subsequent mobility issues.
- Poor balance and coordination: Age-related changes in the vestibular system, vision, and muscle strength can affect balance and coordination, making it harder for seniors to maintain stability and avoid falls.
B. Fractures and Trauma
Fractures and traumatic injuries can severely impact an elderly person’s mobility and overall well-being.
- Hip fractures: Elderly people frequently suffer this injury after falls or accidents. The recovery process after a hip fracture can be challenging, requiring significant rehabilitation and potentially leading to long-term mobility limitations.
- Spinal cord injuries: Spinal cord injuries can occur due to accidents, falls, or other traumatic events. Such injuries can result in partial or complete paralysis, profoundly impacting mobility and independence.
Lifestyle Factors

Certain lifestyle factors can contribute to mobility issues in the elderly, emphasizing the importance of proactive measures to promote mobility and prevent limitations.
A. Sedentary Lifestyle
Leading a sedentary lifestyle with limited physical activity can lead to muscle weakness, reduced flexibility, and overall deconditioning, affecting mobility.
- Lack of physical activity: Insufficient physical activity leads to muscle atrophy, decreased cardiovascular endurance, and reduced bone density. These factors can collectively contribute to mobility limitations in the elderly.
- Prolonged sitting or bed rest: Spending protracted periods in a sitting or lying position can lead to muscle stiffness, joint contractures, and decreased muscle strength, making mobility more challenging.
B. Poor Nutrition
Nutritional deficiencies and poor dietary choices can have a direct impact on the musculoskeletal system and overall health, potentially affecting mobility.
- Malnourishment: Inadequate intake of essential nutrients can weaken muscles and bones, impairing mobility. Malnourished individuals may experience muscle wasting and increased frailty, making daily activities more challenging.
- Vitamin D deficiency: Maintaining optimal levels of vitamin D is vital for bone health, as low levels can compromise bone strength, leading to increased fracture susceptibility and decreased mobility.
Prevention and Management Strategies
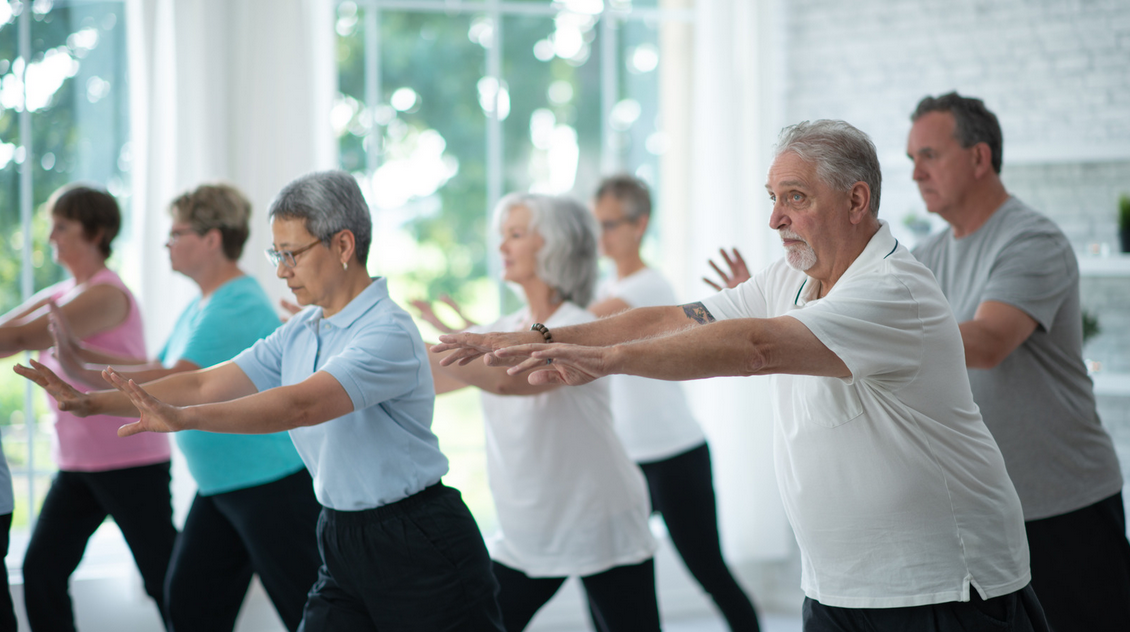

In order to prevent and manage mobility issues in the elderly, various strategies can be employed, focusing on exercise, assistive devices, medications, and environmental safety measures.
A. Regular Exercise and Physical Therapy
Engaging in regular exercise and physical therapy can help improve strength, flexibility, balance, and overall mobility in the elderly.
- Strengthening exercises: Incorporating strength training exercises, including weightlifting and resistance band workouts, into your fitness regimen can notably improve muscle strength, thereby promoting better mobility and reducing the risk of falls.
- Balance and coordination exercises: Specific exercises targeting balance and coordination, like tai chi or yoga, can enhance stability and reduce the risk of falls.
B. Assistive Devices and Home Modifications
Using assistive devices and making appropriate home modifications can significantly improve mobility and safety for the elderly.
- Canes, walkers, and wheelchairs: Depending on individual needs, using assistive devices like canes, walkers, or wheelchairs can provide support and enhance mobility.
- Grab bars and handrails: Installing grab bars in bathrooms and railings on staircases can help seniors maintain balance and prevent falls, promoting safer mobility.
C. Medications and Treatment Options
In some instances, medications and disease-specific treatments can help manage underlying conditions that contribute to mobility issues.
- Pain management: For conditions like osteoarthritis or neuropathy that cause chronic pain, appropriate pain management techniques and medications can improve comfort and mobility.
- Disease-specific treatments: Effective management of chronic diseases like diabetes or COPD can significantly impact mobility. Following prescribed treatments and medications can help mitigate mobility limitations associated with these conditions.
D. Environmental Safety Measures
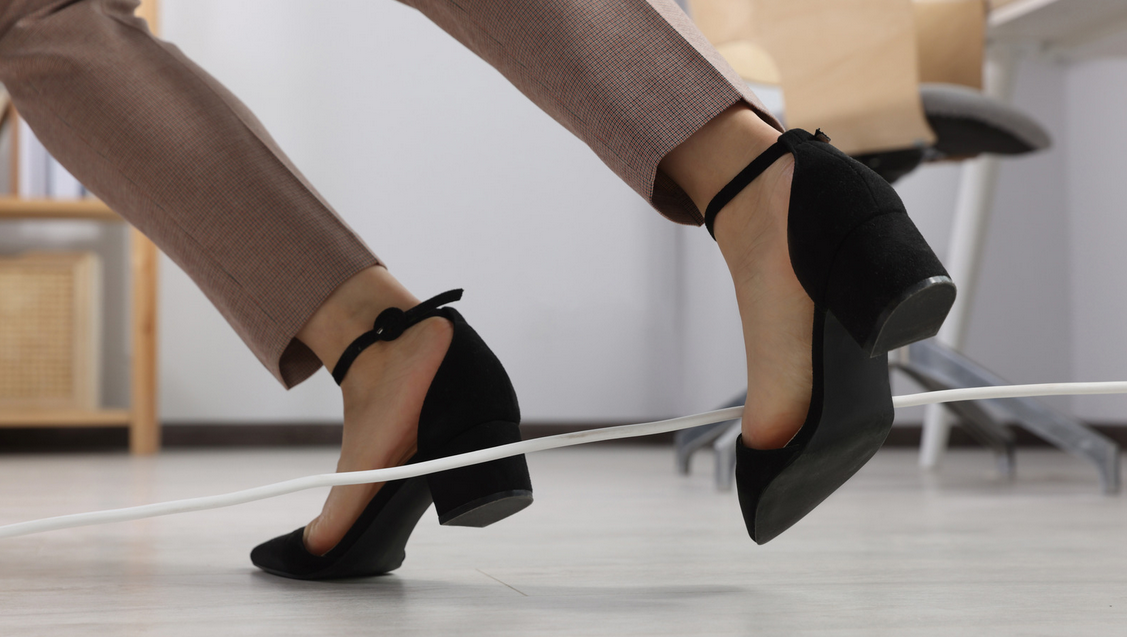

Creating a safe and accessible environment is crucial for preventing falls and promoting mobility in the elderly.
- Removing tripping hazards: Regularly assessing the living space and eliminating tripping hazards, such as loose rugs or clutter, can minimize the risk of falls and subsequent mobility issues.
- Adequate lighting and non-slip surfaces: Ensuring proper lighting and using non-slip surfaces, especially in areas prone to moisture or water, can enhance safety and mobility within the home.
Enhancing Mobility and Quality of Life: Discover the Serenity Senior Care Difference
Ensuring mobility in the elderly is crucial for maintaining independence and high quality of life. By understanding the various causes of mobility issues and implementing preventive and management strategies, seniors can continue to enjoy active and fulfilling lives. At Serenity Senior Care, we specialize in providing personalized support and care for seniors facing mobility challenges.
Contact us today at 973-338-0124 to learn how we can help enhance mobility and overall well-being for your loved ones. Experience the difference with Serenity Senior Care and empower your loved ones to live life to the fullest.


